System characteristics
In a pumping system, the objective, in most cases, is either to transfer a liquid from a source to a required destination, e.g. filling a high level reservoir, or to circulate liquid around a system, e.g. as a means of heat transfer.
A pressure is needed to make the liquid flow at the required rate and this must overcome losses in the system. Losses are of two types: static and friction head.
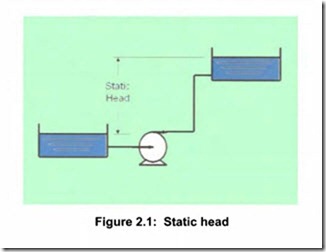
Static head is simply the difference in height of the supply and destination reservoirs, as in Figure 2.1. In this illustration, flow velocity in
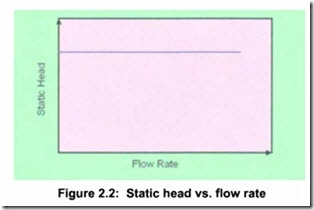
the pipe is assumed to be very small. Another example of a system with only static head is pumping into a pressurized vessel with short pipe runs. Static head is independent of flow rate and graphically would be shown as in Figure 2.2.
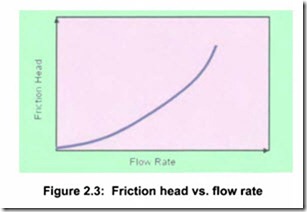
Friction head (sometimes called dynamic head loss) is the friction loss, on the liquid being moved, in pipes, valves and equipment in the system. These losses are proportional to the square of the flow rate. A closed loop circulating system without a surface open to atmospheric pressure, would exhibit only friction losses and would have a system head loss vs. flow characteristic curve as Figure 2.3. This is known as a system curve.