Nomenclature
The notation used throughout the book is given here for general reference as it presents the style adopted and the form of SI units used in one place. Where equations are developed in the book an abbreviated notation will also be given for reference at the point of use.
Note
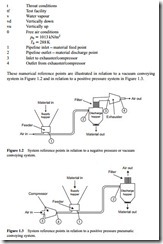
(a) In a negative pressure system, p1 will be slightly below atmospheric pressure if an artificial resistance is added to the air supply pipeline inlet for the purpose of assisting the feed of material into the pipeline; p2 and T2 will generally be equal to p3 and T3; but the mass flow rate of air at 3 might be higher than that at 2 if there is a leakage of air across the material outlet valve on the discharge hopper.
(b) In a positive pressure system; p1 will generally be equal to p4 unless there is a pressure drop across the feeding device; p2 and p3 will generally be equal to the local atmospheric pressure; and the mass flow rate of air at 1 will be lower than that at 4 if there is a leakage of air across the feeding device.