General types of fluids
Petroleum-based fluids
The first major category of hydraulic fluids is the petroleum-based fluid, which is the most widely used type. The crude oil that is quality refined can be used for light services.
Additives should be added to these fluids in order to maintain the following characteristics:
• Good lubricity
• High viscosity index
• Oxidation resistance.
The primary disadvantage of a petroleum-based fluid is that it is flammable. In order to take care of this, fire-resistant hydraulic fluids have been developed, as already discussed in the beginning.
Lubricating oils
These are conventional engine type oils. Due to their better lubricating properties, they enhance the life of the hydraulic components. These oils contain anti-wear additives used to prevent engine wear on cams and valves. Their improved lubricity also provides wear resistance to heavily loaded hydraulic components such as pumps and valves.
Air
Air is also one of the fluids used in hydraulic systems. However, systems that use air as the medium are known as pneumatic systems. The advantages of using air are:
• Air does not burn.
• It can be easily made available in a clean form by the use of filters.
• Any leakage of air from the system is not messy as it simply breaks into the atmosphere.
• Air can also be made into an excellent lubricator by adding a fine mist of oil using a lubricator.
• Use of air in the system eliminates the return lines as air can be simply exhausted back to the atmosphere.
Air also has certain major disadvantages, some of them being:
• Its compressibility
• Its sluggishness and lack of rigidity
• Its corrosivity on account of the presence of oxygen and water.
To summarize, the single most important component in a fluid power system is the working fluid. No single fluid contains all the ideal characteristics required. The designer
should select the fluid having the properties closest to that required by a particular application.
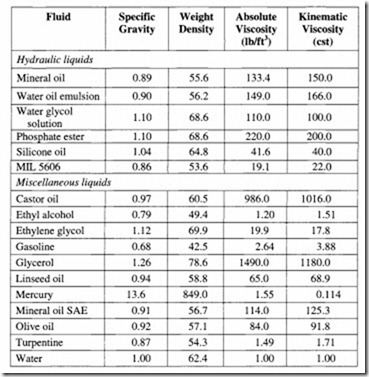
The properties of some of the common hydraulic fluids are tabulated below: