Methods of controlling a rotodynamic pump
The methods of controlling a pump for varying duty are covered in more detail in other sections, but as an introduction to control principles a summary is presented.
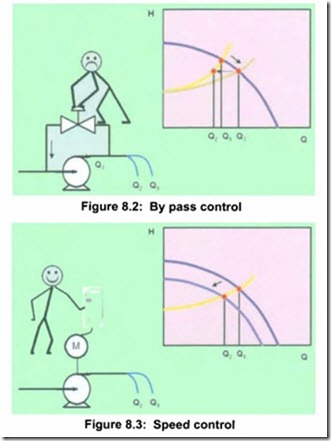
When the user wants to reduce the flow in a process, valve control (see Figure 8.1) can be used either to directly throttle, or control a bypass (see Figure 8.2). Alternatively, speed control (see Figure 8.3) can be applied using a VSD.
Valve control will effectively reduce the flow, however, the consumed energy is often significantly lower if speed control is used. On-off control can be used to vary pumped volume in systems where an intermittent flow
is acceptable . These systems often require a storage facility.
If there is a static head in the pumping system, a substantial amount of energy may be used for lifting, compared with the energy required to overcome the friction in the pipes. Only small speed variations are possible and although energy savings can still sometimes be achieved, applications must be individually evaluated.
In many pumping applications several pumps are used in parallel to produce the required flow when the flow demand varies substantially (typically water and waste water systems) . See Section 4 .2.2.3.