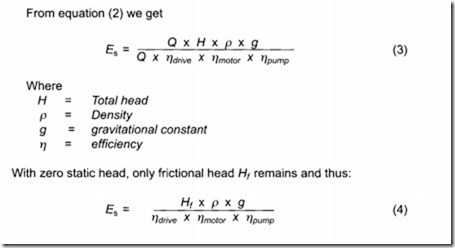
Systems without static head or closed loop systems
The specific energy here is dependent on the frictional head loss which, in turn, is determined by the losses in the pipe system (including throttling valves), and by the combined drive-motor-pump efficiency.
The combined drive-motor-pump efficiency has to be evaluated for each duty point. It is to be noted that the pump efficiency remains approxi mately the same in a system of this type when the speed is changed, whereas the drive-motor efficiency can drop drastically as the load is reduced. If on the other hand, the system curve is changed by changing the setting of a valve, this will change the duty point of the pump and, hence, its efficiency.
Related posts:
Air only relationships:Air flow rate control
THE COMPRESSOR:AIR RECEIVERS
Basic principles:nomenclature and units
Conveying characteristics:The determination of conveying characteristics
MAINTENANCE OF HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS:ROOT CAUSE FAILURE ANALYSIS
ROUBLESHOOTING HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS:ISOLATING PROBLEMS IN A HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT
HYDRAULIC FLUIDS:Density and Specific Gravity
BASIC HYDRAULICS:STATES OF MATTER.
LINES, FITTINGS, AND SEALS:TYPES OF FITTINGS AND CONNECTORS
Fault-finding instruments.
Air Compressors, Air Treatment and Pressure Regulation
THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS:ENERGY BALANCE FOR CLOSED SYSTEMS
SUMMARY OF THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
FORCED CONVECTION: PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF CONVECTION
SUMMARY OF FORCED CONVECTION