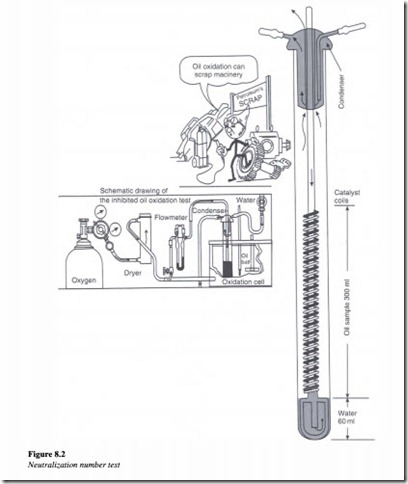
Neutralization number
The neutralization number is a measure of the relative acidity or alkalinity of a hydraulic fluid and is specified by the pH level. A fluid having a smaller neutralization number is recommended, as high-acidity or high-alkaline fluid can cause corrosion of metal parts as well as a deterioration of seal and packing glands.
For an acidic fluid, the neutralization number equals the number of milligrams (mg) of potassium hydroxide necessary to neutralize the acid in a 1 g sample. In the case of an alkaline fluid, the neutralization number equals the amount of alcoholic hydrochloric acid that is necessary to neutralize the alkali in a 1 g sample of hydraulic fluid. With use, hydraulic fluid normally has a tendency to become more acidic than basic.
The neutralization number of a hydraulic fluid can be determined by the following test procedure as illustrated by Figure 8.2.
The oil sample is placed in a titration solution of distilled water, alcohol, toluene and an indicating agent known as naphthol benzene, which changes color from orange to green when neutralization occurs.
Alcoholic potassium hydroxide is added from a burette drop by drop, until the solution changes its color from orange to green. The neutralization number is then calculated using the following formula,
Hydraulic fluids, which have been treated with additives in order to inhibit the formation of acids, are usually able to keep this number at a low value of 0 or 0.1.