Inducted contaminants
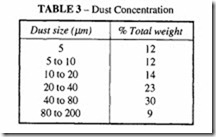
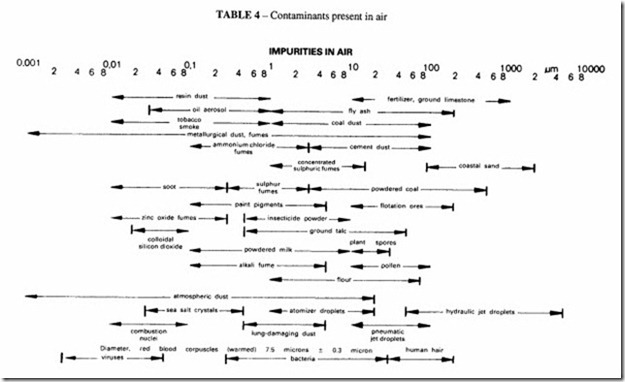
Industrial stationary compressors are normally installed in separate rooms away from factory contaminants, drawing in air from the outside atmosphere as in Figure 3. The level of dust concentration is likely to be of the order of I0-50 mg/m 3• It is standard practice to fit the compressor with an intake filter, having an efficiency of the order of 99.9%, based on the dust concentration present in the ambient air (see Tables 3 and 4). The intake filter can be expected to pass all particles smaller than 5 micron as well as a proportion of the larger sizes. It will also pass atmospheric water vapour and all gases, bacteria and viruses.
Types of intake filters
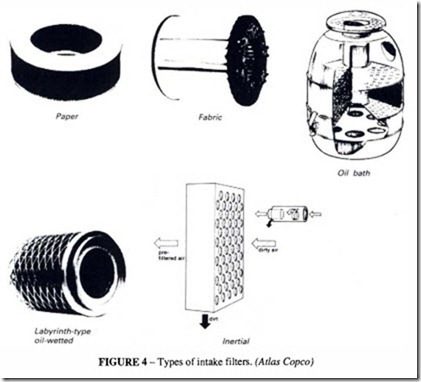
Intake filters (Figure 4) commonly used are:
• Paper filters- with renewable elements used on all types of compressors. Filtering efficiency is high (over 99%) with a typical pressure drop of 2.5 to 3.5 mbar if correctly sized. They are not recommended for use with reciprocating compressors
unless a pulsation chamber is incorporated between the filter and the compressor intake. They are not suitable for handling air in excess of 80°C.
• Fabric filters – stronger than paper and generally cleanable by back flow of compressed air and sometimes by washing.
• Oil bath filters- which have a higher solid retention capability than the above, with a capacity for collecting impurities equal to the mass of the oil. They are not suitable for use on piston compressors unloaded by closing the air inlet valve, unless installed with a bypass or check valve to prevent oil being blown back out of the filter with reversed air flow.
• Labyrinth type oil wetted filters- mostly used on small compressors inducting relatively clean air. They require periodic cleaning.
• Inertial filters – reverse flow or cyclonic, suitable for coarse filtering of large volumes of air. They are normally used as pre-filters in conjunction with one of the other types mentioned above.
The intake filter is normally specified by the compressor manufacturer based on the operating conditions.