Venturi analysis
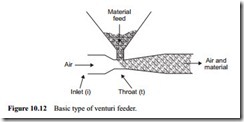
Particular advantages of using venturi feeders for positive pressure conveying lines are that minimum headroom is required, there are no moving parts and, if the device is correctly designed, there need be no air leakage from the feeder, as there is with nearly all other types of feeder. A venturi basically consists of a controlled reduction in pipeline cross section in the region where the material is fed from the supply hopper, as shown in Figure 10.12.
A consequence of this reduction in flow area is an increase in the entraining air velocity, and a corresponding decrease in pressure, in this region. With a correctly designed venturi the pressure at the throat should be just a little lower, or about the same, as that in the supply hopper which, for the majority of applications, is atmospheric pressure. This then encourages the material to flow readily under gravity into the pipeline, and under these conditions there will be no leakage of air from the feeder in opposition to the material feed.
For low pressure applications, in order to keep the throat at atmospheric pressure, and also of a practical size such that it will allow the passage of material to be conveyed, a relatively low limit has to be imposed on the air supply pressure. These feeders, therefore, are usually incorporated into systems that are required to convey free-flowing materials at low flow rates over relatively short distances.
Since only low pressures can be used with the basic type of venturi operating at atmospheric pressure, a positive displacement blower or a standard industrial fan is all that is needed to provide the air. To fully understand the limitations of this type of feeder, the thermodynamic relationships are presented below. The two parameters of interest in venturi feeders are the velocity at the throat and the area, or diameter, of the throat. From the steady flow energy equation, equating between the inlet (i) and the throat (t) gives:
Atmospheric pressure applications
Although venturis capable of feeding materials into conveying pipelines with operating pressure drops of 0.4 bar are commercially available, the additional pressure drop across the venturi can be of the same order. This means that the air supply pressure will have to be at about 0.8 bar gauge and consequently, for this type of duty, it would be recommended that the air should be supplied by a positive displacement blower.
High pressure applications
It was mentioned in Chapters 3 and 4, dealing with feeding devices for pneumatic con- veying systems that with the use of lock hoppers (see Section 4.5) venturis could also be used in high pressure systems. Although the above analysis was used to illustrate the atmospheric pressure application, the same models can be used to analyse high pressure applications simply with an alternative value of the pressure at the throat, pt.