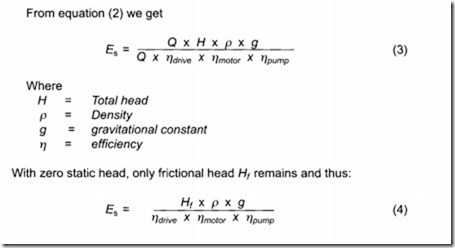
Systems without static head or closed loop systems
The specific energy here is dependent on the frictional head loss which, in turn, is determined by the losses in the pipe system (including throttling valves), and by the combined drive-motor-pump efficiency.
The combined drive-motor-pump efficiency has to be evaluated for each duty point. It is to be noted that the pump efficiency remains approxi mately the same in a system of this type when the speed is changed, whereas the drive-motor efficiency can drop drastically as the load is reduced. If on the other hand, the system curve is changed by changing the setting of a valve, this will change the duty point of the pump and, hence, its efficiency.
Related posts:
Energy and Efficiency:Output energy available
System selection considerations:System economics and Material considerations
ACTUATORS:Piston- Type Cylinders
BASIC DIAGRAMS AND SYSTEMS:FLUID POWER SYSTEMS
Health and safety:Explosion protection
First approximation design methods:Operating point and Solids loading ratios.
Design procedures:Logic diagram for system design
Applications of hydraulic systems:Advantages of hydraulic systems
Hydraulic pumps:Pump performance
Hydraulic pumps:Pump selection
The flapper-nozzle.
Fundamental Principles:Pressure measurement
Safety, Fault-Finding and Maintenance:safety
THE SECOND LA W OF THERMODYNAMICS:HEAT ENGINES
THE SECOND LA W OF THERMODYNAMICS:THE CARNOT REFRIGERATOR AND HEAT PUMP