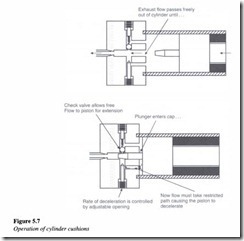
Cylinder cushioning
The end caps are generally made of cast iron or cast aluminum and incorporate threaded entries for ports. End caps have to withstand shock loads at the extreme ends of piston travel. These loads arise not only from fluid pressure, but also from the kinetic energy of the moving parts of the cylinder and load. These shock loads can be reduced with cushion valves built in the end caps.
The cylinder cushioning effect has been illustrated in Figure 5.7.
As shown in the figure, deceleration starts when the tapered plunger enters the opening in the cap resulting in a restriction in exhaust flow, from the barrel to the port. During the final small leg of the stroke, the oil must exhaust through an adjustable opening. The cushion design also incorporates a check valve in order to allow free flow to the piston during reversal in direction.
Consideration should be given to the maximum pressure developed by the cushions at the ends of the cylinder since any excessive pressure build-up would end up rupturing the cylinder.