The Ideal Gas Law
The relationship between mass and volumetric flow rate, pressure and temperature for a gas can be determined from the Ideal Gas Law:
where p is the absolute pressure of gas (kN/m2), is the actual volumetric flow rate of the gas at the pressure p (m3/s), m is the mass flow rate of gas (kg/s), R is the character- istic gas constant (kJ/kg . K) and T is the absolute temperature of gas (K) t°C + 273.
where R0 is the universal gas constant kJ/kg (mol . K) 8.3143 kJ/kg-mol . K and M is the molecular weight (mol).
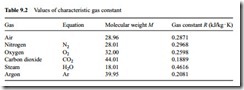
Values for air and some commonly employed gases are presented in Table 9.2. Whichever gas is used, the appropriate value of R for that gas is simply substituted into Equation (9.4) and the design process is exactly the same.
The use of nitrogen
It will be noticed that there is little more than 3 per cent difference between the values of R for air and nitrogen, since about 78 per cent of air, by volume, is nitrogen. As a consequence little error would result if a system was inadvertently designed on the basis of air, and nitrogen was used for conveying the material instead. If carbon diox- ide or superheated steam was to be used to convey the material, however, there would be a very significant error.