DIRECTIONAL CONTROL VALVES
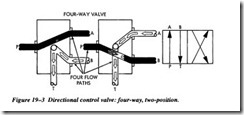
Directional control valves are used to control the operation of pneumatic cylinders and air motors. The most commonly used have moving inner spools or piston slide valves. Moving the spool changes the airflow patterns by redirecting the output to perform different functions. Figure 19-3 depicts the simplified flow pattern through the valve.
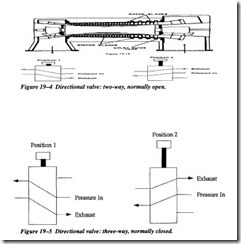
The simplest type of valve is a two-way valve . With this type of valve there are two ports (ports are simply openings for air to pass through) . In one position this valve
will allow air passage. In the other position it allows no flow. Figure 19-4 shows the function of a two-way valve.
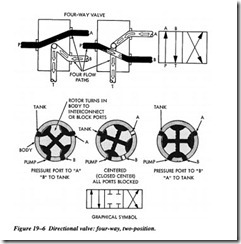
Three-way valves usually have three ports. Pressure goes in one port and is shifted between the other two ports by the spool or piston slide valve. This type of valve is typically used when high cylinder speeds are needed or spring return cylinders are used. Figure 19-5 shows the function and flow through three-way valves.
Four-way valves are probably the most common type of directional control valve. Their porting allows cylinders and air motors to be reversed. Some four-way valves have four ports (only one exhaust) and some have five ports (two exhausts). An advantage of the five-port valve is its capability to control exhaust flow from two exhaust ports. This allows the extension and retraction speed of a cylinder to be controlled independently. Figure 19-6 shows the functions of the five different ports.