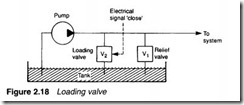
Loading valves
Expression 2.2 shows that allowing excess fluid from a pump to return to the tank by a pressure relief valve is wasteful of energy and can lead to a rapid rise in temperature of the fluid as the wasted energy is converted to heat. It is normally undesirable to start and stop the pump to match load requirements, as this causes shock loads to pump, motor and couplings.
In Figure 2.18, valve V1 is a normal pressure relief valve regulating pressure and returning excess fluid to the tank as described in earlier sections. The additional valve V2 is opened or closed by an external electrical or hydraulic signal. With valve V2 open, all the pump output flow is returned to the tank at low pressure with minimal energy cost.
When fluid is required in the system the control signal closes valve V2, pressure rises to the setting of valve V 1, and the system performs as normal. Valve V2 is called a pump loading or a pump unloading valve according to the interpretation of the control signal sense.