Graphic symbols
Simple valve symbols have been used so far to describe control actions. From the discussions in the previous section it can be seen that control actions can easily become too complex for representation by sketches showing how a valve is constructed.
A set of graphic symbols has therefore evolved (similar, in principle, to symbols used on electrical circuit diagrams). These show component function without showing the physical construction of each device. A 3/2 spool valve and a 3/2 rotary valve with the same function have the same symbol; despite their totally different con structions.
Symbols are described in various national documents; DIN24300, BS2917, IS01219 and the new IS05599, CETOP RP3 plus the original American JIC and ANSI symbols. Differences between these are minor.
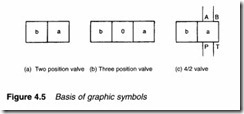
A valve is represented by a square for each of its switching positions. Figure 4.5a thus shows the symbol of a two position valve,and Figure 4.5b a three position valve. Valve positions can be rep resented by letters a, b, c and so on, with 0 being used for a central neutral position.
Ports of a valve are shown on the outside of boxes in normal unoperated or initial position. Four ports have been added to the two position valve symbol shown in Figure 4.5c. Designations given to ports are normally:
ISO 5599 proposes to replace these letters with numbers, a retro grade step in the author’s opinion.
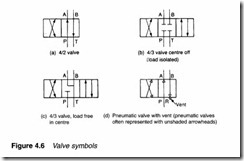
Arrow-headed lines represent direction of flow. In Figure 4.6a, for example fluid is delivered from port P to port A and returned from port B to port T when the valve is in its normal state a. In state b, flow is reversed. This valve symbol corresponds to the valve rep resented in Figures 4.2 and 4.3a.
Shut off positions are represented by T, as shown by the central position of the valve in Figure 4.6b, and internal flow paths can be represented as shown in Figure 4.6c. This latter valve, incidentally, vents the load in the off position.
In pneumatic systems, lines commonly vent to atmosphere directly at the valve, as shown by port R in Figure 4.6d.
Figure 4.7a shows symbols for the various ways in which valves can be operated. Figure 4.7b thus represents a 4/2 valve operated by a pushbutton. With the pushbutton depressed the ram extends. With the pushbutton released, the spring pushes the valve to position a and the ram retracts.
Actuation symbols can be combined. Figure 4.7c represents a solenoid-operated 4/3 valve, with spring return to centre.
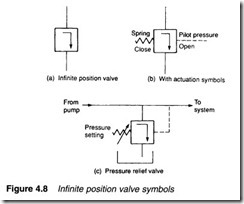
Infinite position valve symbols are shown in Figure 4.8. A basic valve is represented by a single square as shown in Figure 4.8a, with the valve being shown in a normal, or non-operated, position. Control is shown by normal actuation symbols: in Figure 4.8b, for example, the spring pushes the valve right decreasing flow, and pilot pressure pushes the valve left increasing flow. This represents a pressure relief valve which would be connected into a hydraulic system as shown in Figure 4.8c.