OTHER DVC SYSTEMS
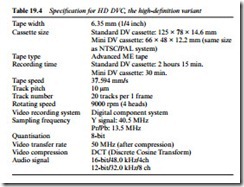
There are four primary standards in the DVC format. ATV, for use with the US Advanced TV System, offers high-definition digital TV, while DVB is for use with the sort of digital broadcast system described in Chapter 12 of this book. SD has been the subject of this chapter; its specification was given in Table 19.3. HD is the high- definition variant for which the specification is given in Table 19.4.
The main differences between HD and SD variants is the tape speed, twice as fast giving half the running time; the four-head drum; and a picture resolution capability approaching 1500 lines.
Related posts:
Magnetic tape recording:The complete VCR and UHF tuner and IF amplifier
Flat panel television receivers:Zero voltage switching
AERIALS AND RECEIVERS:DISTRIBUTION AMPLIFIERS FOR UHF,SATELLITE AERIALS,TUNERS AND VARICAP TUNING.
IC FIELD TIMEBASE
Digital recording and camcorder:Rendering and DV Editing
SERVO SYSTEMS:TILTING DRUM TECHNOLOGY.
VIDEO ON MAGNETIC TAPE:FM MODULATION.
VIDEO DISC TECHNOLOGY:BEAM FOCUS SERVO.
Magnetic tape recording:Down-conversion
The digital TV reception:The boot-up sequence
DVD:Focus depth and numerical aperture
MPEG encoding:AVC motion compensation
DVD:Dolby digital (AC-3) encoding.
SERVO SYSTEMS:SERVO AND MOTOR FAULT SYMPTOMS.
VIDEO DISC TECHNOLOGY:LIGHT PATH.