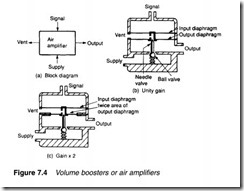
Volume boosters
An air amplifier is illustrated in Figure 7.4. It is provided with an air supply (typically 2-4 bar) and an input signal pressure. The amplifier admits air to, or vents air from, the output to maintain a
constant output/input ratio. An amplifier with a gain of two, for example, turns a 0.2 to 1 bar signal range to a 0.4 to 2 bar range. Output pressure, controlled by the amplifier, has the ability to provide a large air volume and can drive large capacity loads.
A unity gain air amplifier is shown in Figure 7.4b. It consists of two equal-area linked diaphragms, which together operate a needle and ball valve arrangement. The low volume input signal is applied to the upper diaphragm and the output pressure to the lower diaphragm. If output pressure is lower than inlet pressure, the diaphragm is pushed down, closing needle valve and opening ball valve to pass supply air to the load and increase output pressure.
If the output pressure is high, the diaphragm is forced up, closing the spring-loaded ball valve and opening the needle valve to allow air to escape through the vent and reduce output pressure. The amplifier stabilises with output and input pressures equal.
The input port has a small and practically constant volume, which can be controlled directly by a flapper-nozzle. The output pressure tracks changes in inlet pressure, but with the ability to supply a large volume of air.
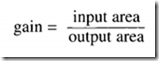
An air amplifier balances when forces on the two diaphragms are equal and opposite. Equal area diaphragms have been used in the unity gain amplifier of Figure 7.4b. The area of the input diaphragm in the amplifier of Figure 7.4c is twice the area of the output diaphragm. For balance, the output pressure must be twice the input pressure, giving a gain of two. In general, the amplifier gain is given by: