OTHER DVC SYSTEMS
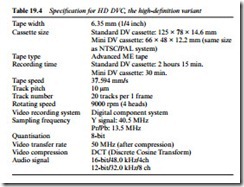
There are four primary standards in the DVC format. ATV, for use with the US Advanced TV System, offers high-definition digital TV, while DVB is for use with the sort of digital broadcast system described in Chapter 12 of this book. SD has been the subject of this chapter; its specification was given in Table 19.3. HD is the high- definition variant for which the specification is given in Table 19.4.
The main differences between HD and SD variants is the tape speed, twice as fast giving half the running time; the four-head drum; and a picture resolution capability approaching 1500 lines.
Related posts:
Television receivers and colour processing:Colour burst processing
Channel encoding:Terrestrial channel encoder
TV CAMERAS AND ANALOGUE COLOUR ENCODING:COLOUR TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION.
TIMEBASE CIRCUITS.
IMAGE DISPLAY AND CAPTURE DEVICES:PURITY ADJUSTMENT
Video re-production:Extra high tension
Flat panel television receivers:HDMI operation
POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS:IC-BASED SMPSU.
TAPE DECK MECHANICS AND SERVICING:TAPE PATH
Magnetic tape recording:Audio signal processing
Video re-production:Raster geometry
TV sound, mono and NICAM:DQPSK decoder
Projection systems:Colour filter less 3-panel HTPS projector
SATELLITE TELEVISION:HEAD-END UNITS
TEST EQUIPMENT AND FAULT DIAGNOSIS:TEST EQUIPMENT.