Quadrature amplitude modulation
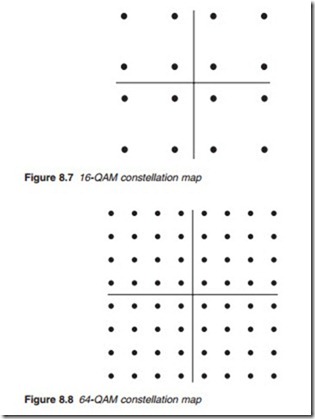
QAM is an extension of PSK in that some phasors are changed in amplitude as well as phase to provide increased bit representation. For instance, 16-QAM encoding increases the bit width of the modulation to 4 as shown in Figure 8.6. Twelve different carrier phasors are used, four of which have two amplitudes to provide further 4-bit combinations. Figure 8.7 depicts all possible carrier phase angles and amplitudes; it is known as a constel- lation map.
A higher order of digital modulation may be employed, for example, in cable, namely 64-QAM encoding, in which each carrier phase/amplitude represents one of 64 possible 6-bit combinations. The constellation map for 64-QAM is shown in Figure 8.8.
Related posts:
Plasma panels:Selective erase addressing
DIGITAL TV:MULTIPLEXING,CONDITIONAL ACCESS AND MODULATION SYSTEMS.
Flat panel television receivers:Scan-rate conversion.
Magnetic tape recording:Down-conversion
TV sound, mono and NICAM:Receiver circuit
CONTROL SYSTEMS:ADVANCED REMOTE CONTROLLERS.
MPEG encoding:New entropy coding technology
TIMEBASE SERVICING
Digital recording and camcorder:Rendering and DV Editing
Video re-production:Display units
Digital recording and camcorder:Audio and video capture
Flat panel television receivers:Principle of operation of resonant converters
Plasma panels:Driving the panel
The digital TV reception:Flat panel iDTV
AERIALS AND RECEIVERS:IF AMPLIFIERS