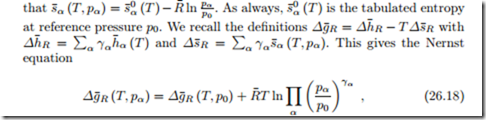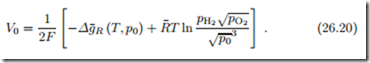Nernst Equation
The Nernst equation describes how the Gibbs free energy of reaction, and thus open circuit voltage and power generation of a fuel cell, depends on the pressures of the reactant and product streams. Indeed, so far we have only considered the temperature dependence of Δg¯R and implicitly assumed that the flows are at reference pressure. Now we consider the more general case, where the in- and outflows have different pressures pα.
To simplify the argument, we assume that all streams are ideal gases, so
where the argument (T, pα) indicates that the in- and outflows are all at the same temperature T , but at different pressures pα.
For a hydrogen fuel cell in which the product is steam, the Nernst equation gives the open circuit potential
If the product water is liquid, the entropy of the water is independent of pressure due to incompressibility, s¯H2 0 (T, pH2 O ) = s¯H2 0 (T ), and the open circuit potential is
These two equations show that the open circuit voltage can be increased by supplying fuel (H2) and oxidizer (O2) at elevated pressures. When the product is steam, lowering the steam pressure increases the open circuit voltage.