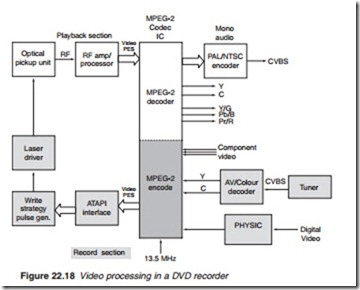
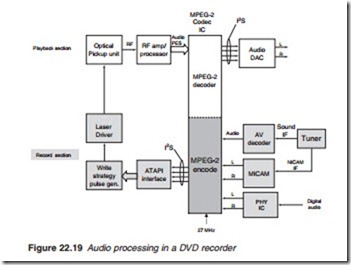
DVD recorder
A DVD recording system consists of two major sections: AV playback/ record (PB/REC) and servo-control. The servo-control and AV playback are described in detail in chapter 21. In the video playback mode, RF sig- nals from the optical pickup unit (OPU) is amplified and processed to pro- duce MPEG-2 PESs (packetised elementary streams) that are decoded by the MPEG-2 decoder to produce analogue video signal in the form of com- ponent video or Y/C a shown in Figure 22.18. Composite video (CVBS) is also available from the PAL/NTSC encoder. In the record mode, analogue video from a tuner via a colour decoder, or direct component video are first MPEG-2 encoded to produce video PESs that are fed into the write strategy pulse generator via an ATAPI interface and hence forth to the blue laser driver. ATAPI which stands for AT Attachment Packet Interface (AT is advanced technology) is a standard interface between a PC or other computer-controlled devices on the one hand and CD/DVD or tape
backup drives on the other. It is based on the IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics interface) specifications used for HDDs with some additional commands needed for controlling a CD/DVD or tape drive. Where the video input is digital, a PHY (pronounced fi and stands for physical layer in the OSI communication model, see Appendix A5) IC is used. The PHY chip is a fast (400 Mbps) Transreceiver which acts as an interface between digital and analogue domains.
A similar process is applied to the audio signals in the playback and record modes as shown in Figure 22.19. The playback is the same as that described in Chapter 20. In the record mode, mono or stereo audio is MPEG-2 encoded by the MPEG-2 codec chip. PCM sound from the MPEG-2 encoder goes to the ATAPI interface via sound serial bus I2S on its way to the write strategy pulse generator where it is multiplexed with the video signal before going to the laser driver.
HDD recorder
Video processing activities similar to those used in DVD recording are required for recording A/V signals on a HDD where audio and video PESs are stored as files on the disk. A block diagram of a DVD/HDD
recorder using system processor made by LSI Logic is shown in Figure 22.20. DMN 8603 is a system-on-chip IC which provides comprehensive solutions to DVD recorders including DSP servo control and video and audio encoding/decoding with in-built microprocessor. Two ATAPI inter-faces are available, one for the DVD drive and the other for the HDD drive. The HDD itself is the normal IDE-type hard disk with a capacity ranging from 80 GB upwards.
In DVD HD recording, two modes may be used: real time in which the DVD is written to directly and non-real time in which the data bitstream is first recorded into an HDD first and transferred to the DVD at a later stage.