Voltage Regulation
It is clear that with change in load, there is a change in terminal voltage of an alternator. The magnitude of this change depends not only on the load but also on the load power factor.
The voltage regulation of an alternator is defined as “the rise in voltage when full-load is removed (field excitation and speed remaining the same) divided by the rated terminal voltage.”
(ii) In the case of leading load p.f., terminal voltage will fall on removing the full-load. Hence, regulation is negative in that case.
(iii) The rise in voltage when full-load is thrown off is not the same as the fall in voltage when full-load is applied.
Voltage characteristics of an alternator are shown in Fig. 37.29.
Determination of Voltage Regulation
In the case of small machines, the regulation may be found by direct loading. The procedure is as follows :
The alternator is driven at synchronous speed and the terminal voltage is adjusted to its rated value V. The load is varied until the wattmeter and ammeter (connected for the purpose) indicate the rated values at desired p.f. Then the entire load is thrown off while the speed and field excitation are kept constant. The open-circuit or no-load voltage E0 is read. Hence, regulation can be found from
In the case of large machines, the cost of finding the regulation by direct loading becomes prohibitive. Hence, other indirect methods are used as discussed below. It will be found that all these methods differ chiefly in the way the no-load voltage E0 is found in each case.
1. Synchronous Impedance or E.M.F. Method. It is due to Behn Eschenberg.
2. The Ampere-turn or M.M.F. Method. This method is due to Rothert.
3. Zero Power Factor or Potier Method. As the name indicates, it is due to Potier.
All these methods require—
1. Armature (or stator) resistance Ra
2. Open-circuit/No-load characteristic.
3. Short-circuit characteristic (but zero power factor lagging characteristic for Potier method). Now, let us take up each of these methods one by one.
(i) Value of Ra
Armature resistance Ra per phase can be measured directly by voltmeter and ammeter method or by using Wheatstone bridge. However, under working conditions, the effective value of Ra is increased due to ‘skin effect’*. The value of Ra so obtained is increased by 60% or so to allow for this effect. Generally, a value 1.6 times the d.c. value is taken.
(ii) O.C. Characteristic
As in d.c. machines, this is plotted by running the machine on no-load and by noting the values of induced voltage and field excitation current. It is just like the B-H curve.
(iii) S.C. Characteristic
It is obtained by short-circuiting the armature (i.e. stator) windings through a low-resistance ammeter. The excitation is so adjusted as to give 1.5 to 2 times the value of full-load current. During this test, the speed which is not necessarily synchronous, is kept constant.
Example 37.17 (a). The effective resistance of a 2200V, 50Hz, 440 KVA, 1-phase, alternator is 0.5 ohm. On short circuit, a field current of 40 A gives the full load current of 200 A. The electro- motive force on open-circuits with same field excitation is 1160 V. Calculate the synchronous impedance and reactance. (Madras University, 1997)
Solution. For the 1-ph alternator, since the field current is same for O.C. and S.C. conditions
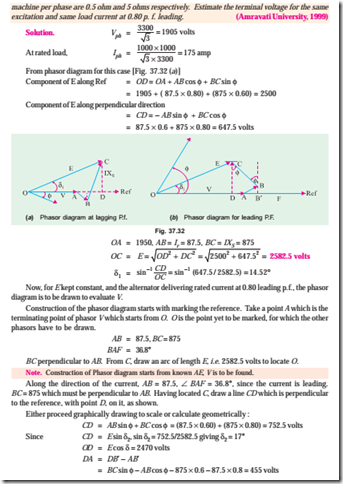
Example 37.17 (b). A 60-KVA, 220 V, 50-Hz, 1-f alternator has effective armature resistance of ohm and an armature leakage reactance of 0.07 ohm. Compute the voltage induced in the armature when the alternator is delivering rated current at a load power factor of (a) unity (b) 0.7 lagging and (c) 0.7 leading.
(Elect. Machines-I, Indore Univ. 1981)
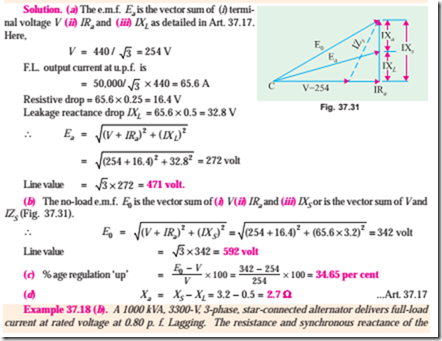
Example 37.18 (a). In a 50-kVA, star-connected, 440-V, 3-phase, 50-Hz alternator, the effective armature resistance is 0.25 ohm per phase. The synchronous reactance is 3.2 ohm per phase and leakage reactance is 0.5 ohm per phase. Determine at rated load and unity power factor :
(a) Internal e.m.f. Ea (b) no-load e.m.f. E0 (c) percentage regulation on full-load (d) value of synchronous reactance which replaces armature reaction.