The HD ready television receiver
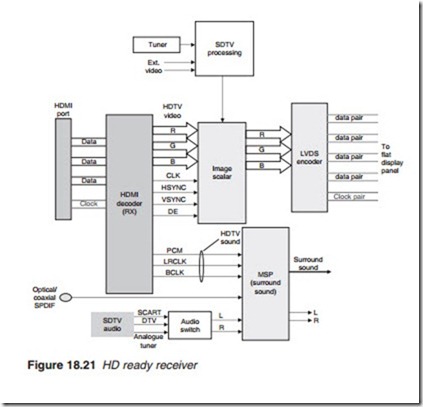
Invariably, the HD receiver is a flat panel television (Figure 18.21). Video and audio data arriving at the HDMI port go to the HDMI decoder (receiver). The HDMI decoder converts the video back to a digital 8-bit RGB together with the clock, H/V sync and enable. The audio PCM (stereo or surround sound) from the HDMI decoder is fed directly to the multi-sound processor (MSP). Sound from other sources such as opti- cal/coaxial SPDIF or a SCART is also fed into the MSP chip. The centre of the receiver is the image scalar which receives HD video from the HDMI decoder and SD video from the SDTV processing section. The purpose of the image-scaling chip is to convert the incoming signals which may have a variety of resolutions (HD or SD video as well as PC-generated video) into a form that is compatible with the native resolution of the plasma or LCD panel. The output of the scalar is fed into a DVI encoder (normally LVDS) to feed the display panel driver boards. The SD video may be in analogue format from an analogue tuner/video processor or a SCART connector or digitised video from a terrestrial DVB SD tuner/demodulator/decoder.
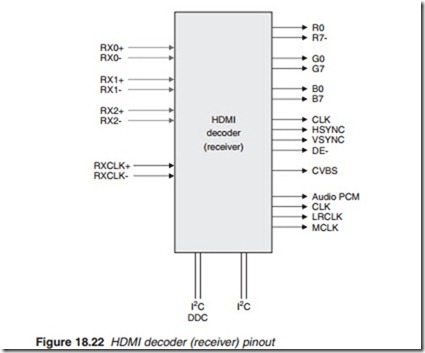
The pin assignment for an HDMI decoder (receiver) chip is outlined in Figure 18.22.