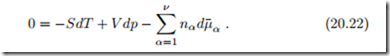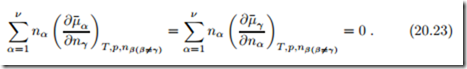Gibbs and Gibbs-Duhem Equations
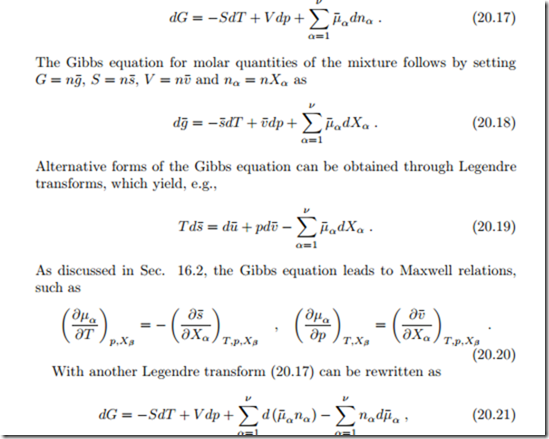
We revisit the Gibbs equation for the mixture (20.1),
which, together with (20.11), yields the Gibbs-Duhem relation
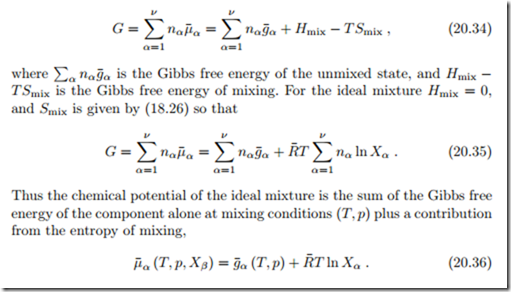
Taking the derivative of the Gibbs-Duhem relation (20.22) with respect to a mole number nγ yields, with the symmetry property (20.16),
Mass Based Chemical Potential
It is an easy exercise to translate the above mole based relations into mass based relations, which read
The Chemical Potential for an Ideal Mixture
The Gibbs free energy of an ideal mixture at (T, p) is given by
The Chemical Potential for an Ideal Gas Mixture
Using that g = h − Ts and the property relations for the ideal gas, the chemical potential of an ideal gas is
Thus, we find the intuitive result that for an ideal gas the partial pressure pν = Xν p is continuous at the ideal semipermeable membrane. This means, that the component that can pass the membrane behaves as if the membrane is not present, it is homogeneously distributed over the entire accessible volume.