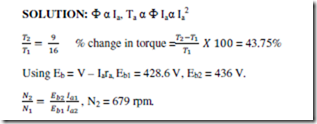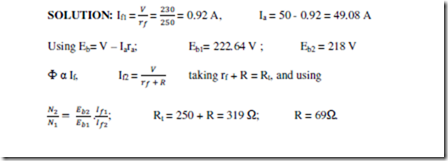PROBLEMS:
1. A 250 V DC shunt motor has shunt field resistance of 150 Ω and armature resistance of 0.6 Ω. The motor operates on No-load with a full field flux at its base speed of 1000 rpm with armature current of 5A. If the machine drives a load requiring a torque of 100Nm, calculate the armature current and
speed of motor. If the motor is required to develop 10 kW at 1200 rpm, what is the required value of the external series resistance in the field circuit? Neglect saturation and armature reaction.
SOLUTION:
2. A 4-pole series wound fan motor draws an armature current of 50A, when running at 2000 rpm on a 230 V DC supply with four coils connected in series. The four field coils are now connected in two parallel groups of two coils in series. Assuming the flux/pole to be proportional to the exciting current and load torque proportional to the square of speed, find the new speed and armature current. Neglect losses. Given: Armature resistance = 0.2 0, resistance of each field coil = 0.05 0.
SOLUTION:
3. A shunt motor runs at 1200 rpm on a 420 V circuit and current taken in 30 A in addition to the field current. What resistance must be placed in series with armature in order that the speed may be reduced to 600 rpm, the current through the armature remaining same.ra = 3Ω given.
4. A 4 pole 230 V series motor runs at 1000 rpm when the load current is 12 A. the series field resistance is 0.8 Ω and the armature resistance is 1Ω. The series field coils are now regrouped from all in series to two in series with two parallel paths. The line current is now 20 A if the corresponding weakening of field is 15 %. Calculate the speed of the motor.
5. A 220 V DC shunt motor runs at 500 rpm when the armature current is 50 A calculate the speed if the torque is doubled. Given ra = 0.2 0.
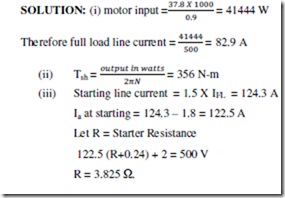
6. A 500 V, 50 BHP (37.8 kW) 1000 rpm DC shunt motor has, on full load an η of 90%. The armature circuit resistance is 0.24 0 and there is a total voltage drop of 2 V at the brushes. The field current is 1.8 A. Determine
(i) Full load line current
(ii) Full load shaft torque
(iii) Total resistance in motor starter to limit the starting current to 1.5 times the full load current.
7. A 460 V series motor runs at 500 rpm taking a current of 40 A. Calculate the speed and % change in torque if the load is reduced, so that the motor is taking 30 A. Total resistance of the armature and field circuit is 0.8 0. Assume flux is proportional to the field current.
8. A 220 V DC series motor is running at a speed of 800 rpm and draws 100 A. Calculate at what speed the motor will run when developing half the torque. Armature + field resistance is 0.1 0. Assume that magnetic circuit is unsaturated.
9. An 8kW 230 V, 1200 rpm DC shunt motor has ra = 0.70. the field current is adjusted until, on NO load with a supply of 250 V, the motor runs at 1250 rpm and draws a armature current of 1.6 A. A load torque is then applied to the motor shaft, which causes the armature current to raise to 40 A and the speed falls to 1150 rpm. Determine the reduction in flux per pole due to the armature reaction.
10. A 230 V, DC shunt motor runs at 800 rpm and takes armature current of 50 A. Find the resistance to be added to the field circuit to increase the speed from 800 rpm to 1000 rpm at an armature current of 80 A. Assume the flux to be proportional to the field current. Given ra = 0.150 and rf = 2500.
Related posts:
Incoming search terms:
- A dc series motor with an unsaturated magnetic circuit and negligible resistance when running at a certain speed on a given load take 50A at 500v if the load torque varies as the cube of the speed find the resistance to be inserted to reduce the speed by
- a shunt motor supplied at 230 v run 900 rpm when the aMmature current 30 A
- The resistance of an armature circuit of a 240v shunt motor is 0 4ohms and its full load speed is 1000rpm Calculate the resistance to be connected in series with the circuit to reduce the speed to 800rpm when the full load current is 50A
- a 220 v dc shunt motor runs at 500 rpm
- A 230v series motor runs at 1200 rpm at a quarter full load torque taking a current of 16A Calculate its speed at half and full-load torque The resistance of the armature brushes and field coils is 0 25 ohms Assume the flux per pole to be proportional to
- if torque varies as cube of speed
- A 200V series motor takes a current of 100A and runs at 1000r p m the total resistance of the motor is 0 1ohm and the field is unsaturated calculate the percentage change in torgue and speed if the load is so changed that motor current is 50A
- a series motor working on 200 v takes 20 a at 1000 rpm find speed parralel with armature
- a dc motor develops of torque 100 nm at 1000 rpm if motor now runs at 1200 rpm the torque will be
- a DC motor develops of torque of 100Nm at 1000rpm if the motor now runs at 1200 rpm the torque will be
- A 460V series motor runs at 500 rpm taking a current of 40 A calculate the speed and percentage change and torque
- a 30hp 240v 1150rpm DC shunt motor operating at rated condition
- calculate the additional resistance required in shunt circuit to raise no load speed to 1000rpm
- if a motor runs at 1200 rpm what would the power of motor ?
- a 220v dc shunt motor run at 500rpm where the armarture current is 50 cslculated the speed if the torque is doubled given that Ra
- a 220 V d c shunt motor runs at 500 rpm when the armature current is 50A calculate the speed if the torque is doubled given that Ra= 0 2
- A 220 v dc motor runs at 500rpm when the armature current is 50A calculate speed if the torque is doubled the armature resiatance is 0 2 ohms
- unsaturated field resistance
- 220 volt dc field coil supply
- a motor drivers 25nm at 1500 rpm it draws 21a from a 200v supply what is its efficiency?
- A Dc shunt motor takws 25arms when running at 1000rpm from a 220V supplied calculate the current taking fron the supplied at the speed if the load torque is halved
- a 120v shunt motor has the following parameters Ra=0 4 ohms Rsh=120 ohms and losses are 240W on the ful load the current is 19 5A and the motor runs at 1200 rpm
- A shunt motor runs at 600 rpm takes 80A at 250V
- 23 33 A (ii) 840 r p m ] 5 A 100-V shunt motor with a field resistance of 50 W and armature resistance of 0 5 W runs at a speed of 1 000 r p m and takes a current of 10 A from the supply If the total resistance of the field circuit is reduced to three qua
- a motor have back emf 110V and armature current 90A when running at 1500 rev/min determine the power and the torque developed with the armature
- armature current for 10 rpm dc motor
- armature resistance of dc motor
- 220 volts DC shunt motor is operating at a speed of 2000 4:40 p m the armature resistance is 1 ohm and armature current is 10 M if the excitation of the machine is reduced by 10% the extra resistance to be put in the armature circuit to maintain the same
- calculate the speed if toque is doubled
- D C series motor with an unsaturated field Negligible resistance when running at a certain speed on a given foal takes 50 amp at 460 torts If the bad torque varies as a cube of the sped calculate the resistance required to reduce the speed by 25%
- DC motor develops a torque at140Nm at 1400 rpm If the motor runs at 100 nm then torque developed will be
- how to calculate rpm
- if saturation is neglected for dc shunt motor then flux is
- a 220 volt shunt motor current of 40 amps and run at 1000 rpm on full load the armature and field resistance are 0 2 and 250 if the resistance 5 is placed in series
- a dc series motor is rated 230 volt 1000rpm 80A the series field
- what is the required value of the external series resistance in the feild
- A 230 V DC shunt motor runs at 800 rpm and takes the armature current of 50 A Find the resistance to be added to the field circuit to increase speed to 1000 rpm at an armature current of 80 A Assume the flux proportional to field current Armature Resistan
- a 230 volt DC motor has an armature resistance of 0 6 ohm
- a 220 v dc shunt motor has an armature resistance of 0 2
- a 250 v dc shunt motor takes a total current of 20 A
- A 250v dc series motor runs at 500 rpm the shaft torqe is 130 N M and the efficiency at this lead is 88% find the current taken by the motor
- a 220 v dc series motor is run at 800 rpm and draw 100q
- A 220 V DC series motor has armature and field resistance of 0 2Ohm and 0 5 Ohm respectively when running at 100 rPm the motor draw 10 A from the supply calculate the tongue? torque?
- a 500v a 37 3kw 1000r p m dc shunt motor has on full load an efficiency of 90%
- A DC electric motor spinning at 4500 RPM draws 3 amps of current with 110 volts measured at its terminals The resistance of the armature windings measured with an ohmmeter when the motor is at rest unpowered is 2 45 ohms How much counter-EMF is the motor
- a dc m motor develops of torque of 100 n-m at 1000 rpm if the motor now runs at 1200 rpm the torque
- a dc motor develop of torque of 100 nm at 1000 rpm if the motor now runs at 1200 rpm the torque will be ?
- a dc motor develops a torque of 100Nm at 1000rpm
- A 640V series motor runs at 500 rpm taking a current of 40A calculate the speed and percentage change in the torque
- A dc motor devlops of torque of 100 Nm at 1000 rpm If the motor naw run at 1200rpm the torque will be ?