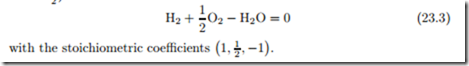Stoichiometric Coefficients
In a chemical reaction, the composition of a mixture changes due to the formation of chemical compounds. The chemical changes are expressed in reaction equations, e.g., for the formation of water from hydrogen and oxygen, where two hydrogen molecules and one oxygen molecule react to form two water molecules,
The first reaction equation uses arrows to indicate the possibility of forward and backward reactions, while the second is written as an actual equation. The coefficients (−2, −1, +2) are the stoichiometric coefficients γα, which count how many particles of species α are involved in the reaction. Positive stoichiometric coefficients refer to products, negative coefficients refer to reactants.
Chemical reactions can occur forward and backward. In chemical equilibrium, the composition of the reacting mixture does not change and there are as many forward as backward reactions. Thus, the definition of “forward” and “backward” is somewhat arbitrary, which implies that the signs of the stoichiometric coefficients can be switched. Moreover, multiplication of all stoichiometric coefficients with the same factor is possible as well, e.g., an alternative chemical equation for the above reaction is (multiplication with − 1/2 )