Gibbs Free Energy of Activation
The law of mass action (24.7) does not allow to identify the reaction rate coefficients kb and kf individually, it only relates their ratio to the Gibbs free energy of reaction. We split the latter into two contributions, the Gibbs free energies of activation for backward and forward reactions, g¯b and g¯f , as
where k0 is a dimensional factor.
Both coefficients are of the form exp where e¯ is an energy (here,the Gibbs free energy of activation). The barometric formula is of the same form, only that there e¯ is the potential energy Mgz. The factor exp r e¯ is know as the Boltzmann factor, it is the typical form of a probability in a thermally activated system.
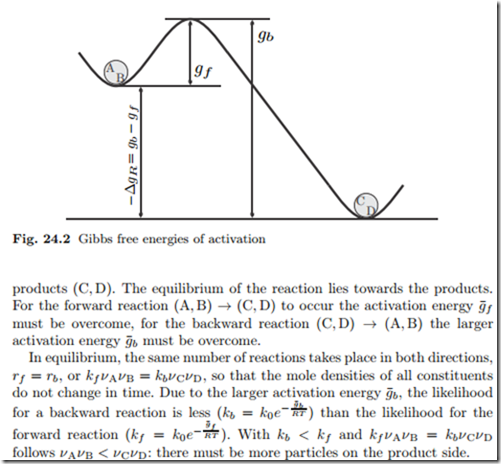
Figure 24.2 shows the Gibbs free energies of activation in an energy land- scape that refers back to Fig. 24.1. The Gibbs free energy of reaction, −Δg¯R, is a measure for the energy difference between the reactants (A, B) and the
The activation energies g¯f , g¯b do not affect the equilibrium, which is described by the Gibbs free energy of reaction Δg¯R in the law of mass action.
However, the activation energies determine how fast the equilibrium will be reached. When the activation energies are large, reactions are unlikely and the reactants will persist in a metastable state, and make no progress towards the final equilibrium state.
The smaller the activation energies divided by temperature, g¯f,b , are, the faster the equilibrium will be reached. Thus, equilibrium will be reached faster at higher temperatures. Fuel in contact with oxygen must be ignited—that is heated to higher T —to overcome the energy barrier at the point of ignition. The released heat then provides the energy to overcome the barrier in the neighborhood, a fast chain reaction occurs.
Catalysts do not take part in the reaction, but their presence lowers the activation energies. Ammonia synthesis provides an example for a reaction that is stuck in a metastable state, and will come to reaction only with the help of catalysts. Even then, to overcome the energy barrier, the temperature must be increased.