Power Developed by a Synchronous Motor
In Fig. 38.21, OA represents supply voltage/phase and Ia = I is the armature current, AB is back e.m.f. at a load angle of a. OB gives the resultant volt- age ER = IZS (or I XS if Ra is negligible). I leads V by f and lags behind ER by an angle q = tan (X S / Ra). Line CD is drawn at an angle of q to A B. AC and ED are ^ to CD (and hence to AE also).
Mechanical power per phase developed in the rotor is
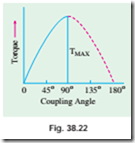
This shows that the maximum power and hence torque (∵ speed is constant) depends on V and Eb i.e., excitation. Maximum value of q (and hence a) is 90º. For all values of V and Eb, this limiting value of a is the same but maximum torque will be proportional to the maximum power developed as given in equation (iii). Equation (ii) is plotted in Fig. 38.22.
Alternative Expression for Power Developed