PROJECT 7.1—Read CID Register and Display on a PC Screen
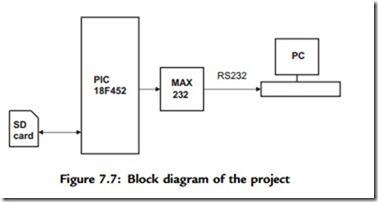
In this project a SD card is interfaced to a PIC18F452-type microcontroller. The serial output port of the microcontroller is connected to the serial input port (e.g.,
COM1) of a PC. The microcontroller reads the contents of the card CID register and sends this data to the PC so it can be displayed on the PC screen.
Figure 7.7 shows the block diagram of the project.
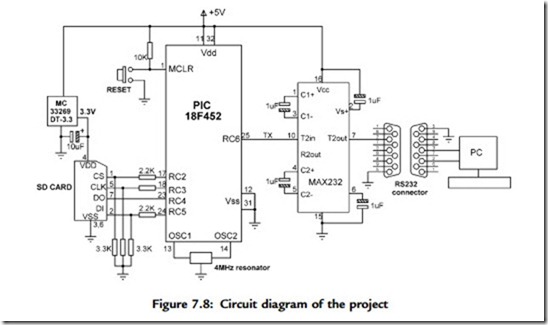
The circuit diagram of the project is shown in Figure 7.8. The SD card is inserted into a card holder and then connected to PORTC of a PIC18F452 microcontroller through 2.2K and 3.3K resistors, using the following pins:
• Card CS to PORTC pin RC2
• Card CLK to PORTC pin RC3
• Card DO to PORTC pin RC4
• Card DI to PORTC pin RC5
According to the SD card specifications, when the card is operating with a supply voltage of VDD ¼ 3.3V, the input-output pin voltage levels are as follows:
• Minimum produced output HIGH voltage, VOH ¼ 2.475V
• Maximum produced output LOW voltage, VOL ¼ 0.4125V
• Minimum required input HIGH voltage, VIH ¼ 2.0625
• Maximum input HIGH voltage, VIH ¼ 3.6V
• Maximum required input LOW voltage, VIL ¼ 0.825V
Although the output produced by the card (2.475V) is sufficient to drive the input port of a PIC microcontroller, the logic HIGH output of the microcontroller (about 4.3V)
is too high for the SD card inputs (maximum 3.6V). Therefore, a potential divider is set up at the three inputs of the SD card using 2.2K and 3.3K resistors. This limits the maximum voltage at the inputs of the SD card to about 2.5V:
Serial output port pin RC6 (TX) of the microcontroller is connected to a MAX232-type RS232 voltage level converter chip and then to a 9-way D-type connector so it can be connected to the serial input port of a PC.
The microcontroller is powered from a 5V supply which is obtained via a 7805-type 5V regulator with a 9V input. The 2.7V–3.6V supply required by the SD card is obtained via an MC33269DT-3.3 regulator with 3.3V output and is driven from the 5V input voltage.
The program listing of the project is given in Figure 7.9 (program SD1.C). At the beginning of the main program, character array CID is declared to have 16 bytes.
Variable msg is loaded with the message that is to be displayed when power is applied to the system. Then the UART is initialized at PORTC with a baud rate of 2400.
Before the SD card library functions are used, the function Spi_Init_Advanced must be called with the given arguments. Then the SD card bus is initialized by calling function Mmc_Init, where it is specified that the card is connected to PORTC. The program then enters an endless loop that repeats every ten seconds.
Inside this loop the heading message is displayed followed by two new-line characters. The program then reads the contents of register CID by calling function Mmc_Read_Cid and stores the data in character array CID. The data is then sent to the serial port by calling function Str_To_Usart. At the end of the loop two new-line characters are displayed, the program waits for ten seconds, and the loop is repeated.
The operation of the project can be tested by connecting the device to a PC and starting the HyperTerminal terminal emulation program on the PC. Set the communications parameters to 2400 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity bit. An example output on the screen is shown in Figure 7.10.