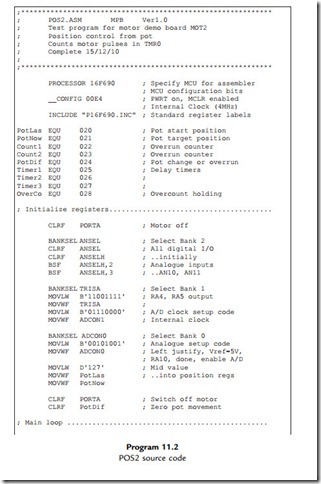
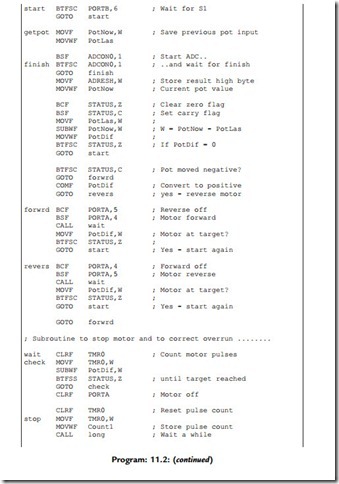
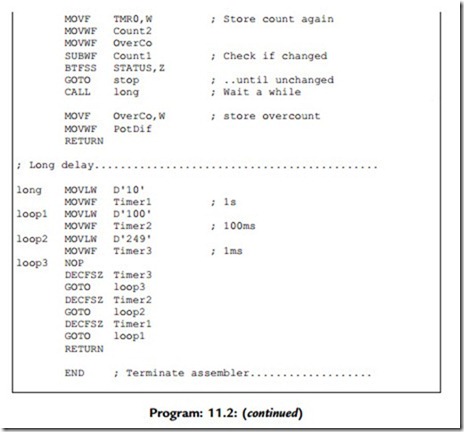
Closed Loop Speed Control
In this example, the motor board is to operate as a slave speed-controlled unit. A master controller supplies an 8-bit code to set the speed of the motor, with the local controller required to maintain it with a specified degree of precision. The MOT2 board allows for a test input at
the switch bank to simulate this external demand. Alternatively, the required speed could be input as a data byte at a serial port.
Suppose that the motor is to be controlled to a speed of exactly 600 rpm. This will produce 10 pulses per second (pps) with a single slot in the wheel. This relatively low speed is used for simulation in ISIS, because the DCM rev counter only reads up to 999 rpm. Real hardware needs to be controlled at speeds up to at least 3000 rpm, using a higher MCU clock speed. The speed can be measured in one of two main ways: by counting sensor pulses over a measured time period, or by measuring the period between sensor pulses.