8279 Programmable Keyboard/Display Controller and Interfacing The Keyboard/Display Controller 8279
Intel’s 8279 is a general purpose Keyboard Display controller that simultaneously drives the display of a system and interfaces a Keyboard with the CPU. The Keyboard Display interface scans the Keyboard to identify if any key has been pressed and sends the code of the pressed key to the CPU. It also transmits the data received from the CPU, to the display device.
Both of these functions are performed by the controller in repetitive fashion without involving the CPU. The Keyboard is interfaced either in the interrupt or the polled mode. In the interrupt mode, the processor is requested service only if any key is pressed, otherwise the CPU can proceed with its main task.
In the polled mode, the CPU periodically reads an internal flag of 8279 to check for a key pressure. The Keyboard section can interface an array of a maximum of 64 keys with the CPU. The Keyboard entries (key codes) are debounced and stored in an 8-byte FIFO RAM, that is further accessed by the CPU to read the key codes. If more than eight characters are entered in the FIFO (i.e. more that eight keys are pressed), before any FIFO read operation, the overrun status is set. If a FIFO contains a valid key entry, the CPU is interrupted (in interrupt mode) or the CPU checks the status (in polling) to read the entry.
Once the CPU reads a key entry, the FIFO is updated, i.e. the key entry is pushed out of the FIFO to generate space for new entries. The 8279 normally provides a maximum of sixteen 7-seg display interface with CPU It contains a 16-byte display RAM that can be used either as an integrated block of 16×8-bits or two 16×4-bit block of RAM. The data entry to RAM block is controlled by CPU using the command words of the 8279.
Architecture and Signal Descriptions of 8279
The Keyboard display controller chip 8279 provides
1. A set of four scan lines and eight return lines for interfacing keyboards.
2. A set of eight output lines for interfacing display.
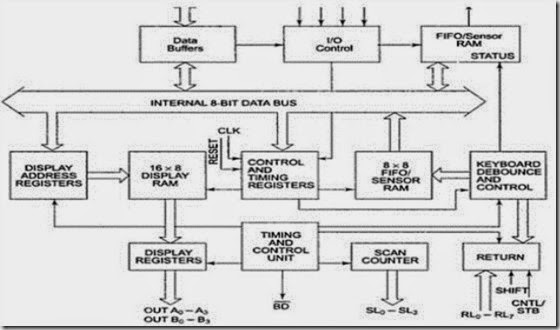
I/O Control and Data Buffer
The I/O control section controls the flow of data to/from the 8279. The data buffer interface the external bus of the system with internal bus of 8279. the I/O section is enabled only if D is low.
8279 Internal Architecture
The pin Ao, RD and WR select the command, status or data read/write operations carried out by the CPU with 8279.
Control and Timing Register and Timing Control
These registers store the keyboard and display modes and other operating conditions programmed by CPU. The registers are written with Ao=1 and WR =0. The timing and control unit controls the basic timings for the operation of the circuit. Scan Counter divide down the operating frequency of 8279 to derive scan keyboard and scan display frequencies.
Scan Counter
The Scan Counter has two modes to scan the key matrix and refresh the display. In the Encoded mode, the counter provides a binary count that is to be externally decoded
to provide the scan lines for keyboard and display (four externally decoded scan lines may drive up to 16 displays).
In the decoded scan mode, the counter internally decodes the least significant 2 bits and provides a decoded 1 out of 4 scan on SL0-SL3 (four internally decoded scan lines may drive up to 4 Displays). The Keyboard and Display both are in the same mode at a time.
Return Buffers and Keyboard Debounce and Control
This section scans for a Key closure row-wise. If it is detected, the Keyboard debounce unit debounces the key entry (i.e. wait for 10 ms). After the debounce period, if the key continues to be detected. The code of the Key is directly transferred to the sensor RAM along with SHIFT and CONTROL key status.
FIFO/Sensor RAM and Status Logic
In Keyboard or strobed input mode, this block acts as 8-byte first-in-first-out (FIFO) RAM. Each key code of the pressed key is entered in the order of the entry, and in the meantime, read by the CPU, till the RAM becomes empty. The status logic generates an interrupt request after each FIFO read operation till the FIFO is empty.
In scanned sensor matrix mode, this unit acts as sensor RAM. Each row of the sensor RAM is loaded with the status of the corresponding row of sensors in the matrix. If a sensor changes its state, the IRQ line goes high to interrupt the CPU.
Display Address Registers and Display RAM.
The Display address registers hold the addresses of the word currently being written or read by the CPU to or from the display RAM. The contents of the registers are automatically updated by 8279 to accept the next data entry by CPU. The 16-byte display RAM contains the 16-byte of data to be displayed on the sixteen 7-seg displays in the encoded scan mode.
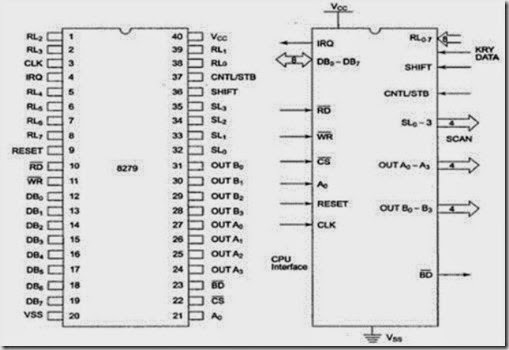
Pin Diagram of 8279 DB0 – DB7 :
These are bidirectional data bus lines. The data and command words to and from the CPU are transferred on these lines.
CLK :
This is a clock input used to generate internal timings required by 8279.
RESET :
This pin is used to reset 8279. A high on this line resets 8279. After resetting 8279, its in sixteen 8-bit display, left entry encoded scan, 2-key lock out mode. The clock prescaler is set to 31.
CS chip select:
A low on this line enables 8279 for normal read or write operations. Otherwise this pin should be high.
Ao :
A high on the Ao line indicates the transfer of a command or status information. A low on this line indicates the transfer of data. This is used to select one of the internal registers of 8279.
RD, WR :
(Input/Output) READ/WRITE input pins enable the data buffer to receive or send data over the data bus.
IRQ:
This interrupt output line goes high when there is data in the FIFO sensor RAM. The interrupt line goes low with each FIFO RAM read operation. However, if the FIFO RAM further contains any Key-code entry to be read by the CPU, this pin again goes high to generate an interrupt to the CPU.
Vss, Vcc :
These are the ground and power supply lines for the circuit.
SL0-SL3 – Scan Lines:
These lines are used to scan the keyboard matrix and display digits. These lines can be programmed as encoded or decoded, using the mode control register.
RL0-RL7 – Return Lines :
These are the input lines which are connected to one terminal of keys, while the other terminal of the keys are connected to the decoded scan lines. These are normally high, but pulled low when a key is pressed.
SHIFT :
The status of the Shift input line is stored along with each key code in FIFO in the scanned keyboard mode. Till it is pulled low with a key closure it is pulled up internally to keep it high.
CNTL/STB-CONTROL/STROBED I/P Mode :
In the Keyboard mode, this line is used as a control input and stored in FIFO on a key closure. The line is a strobe line that enters the data into FIFO RAM, in the strobed input mode. It has an internal pull up. The line is pulled down with a Key closure.
BD – Blank Display :
This output pin is used to blank the display during digit switching or by a blanking command.
OUTA0 – OUTA3 and OUTB0 – OUTB3 :
These are the output ports for two 16×4 (or one 16 x 8) internal display refresh registers.
The data from these lines is synchronized with the scan lines to scan the display and keyboard. The two 4-bit ports may also be used as one 8-bit port.
Modes of Operation of 8279
The Modes of operation of 8279 are
i. Input (Keyboard) modes
ii. Output (Display) modes
Input (Keyboard) modes :
8279 provides three input modes, they are :
1. Scanned Keyboard Mode :
This mode allows a key matrix to be interfaced using either encoded or decoded scans. In the encoded scan, an 8 x 8 keyboard or in decoded scan , a 4 x 8 Keyboard can be interfaced. The code of key pressed with SHIFT and CONTROL status is stored into the FIFO RAM.
2. Scanned Sensor Matrix:
In this mode, a sensor array can be interfaced with 8279 using either encoder or decoder scans. With encoder scan 8 x 8 sensor matrix or with decoder scan 4 x 8 sensor matrix can be interfaced . The sensor codes are stored in the CPU addressable sensor RAM.
3. Strobed Input :
In this mode, if the control line goes low, the data on return lines, is stored in the FIFO byte by byte.
Output (Display) Modes :
8279 provides two output modes for selecting the display options.
1. Display Scan:
In this mode, 8279 provides 8 or 16 character multiplexed displays those can be organized as dual 4-bit or single 8-bit display units.
2. Display Entry:
The Display data is entered for display either from the right side or from the left side.
Details of Modes of Operation Keyboard Modes
1. Scanned Keyboard Mode with 2 Key Lockout
In this mode of operation, when a key is pressed, a debounce logic comes into operation. The Key code of the identified key is entered into the FIFO with SHIFT and CNTL status, provided the FIFO is not full.
2. Scanned Keyboard with N-key Rollover
In this mode, each key depression is treated independently. When a key is pressed, the debounce circuit waits for 2 keyboard scans and then checks whether the key is still depressed. If it is still depressed, the code is entered in FIFO RAM. Any number of keys can be pressed simultaneously and recognized in the order, the Keyboard scan record them.
3. Scanned Keyboard Special Error Mode
This mode is valid only under the N-Key rollover mode. This mode is programmed using end interrupt/error mode set command. If during a single debounce period (two Keyboard scan) two keys are found pressed, this is considered a simultaneous depression and an error flag is set. This flag, if set, prevents further writing in FIFO but allows generation of further interrupts to the CPU for FIFO read.
3. Sensor Matrix Mode
In the Sensor Matrix mode, the debounce logic is inhibited the 8-byte memory matrix. The status of the sensor switch matrix is fed directly to sensor RAM matrix Thus the sensor RAM bits contains the row-wise and column-wise status of the sensors in the sensor matrix.