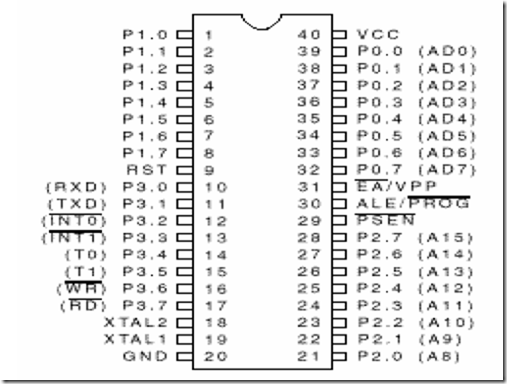
Microcontroller
Contents
•Introduction
•Inside 8051
•Instructions
•Interfacing
Introduction
• Definition of a Microcontroller
• Difference with a Microprocessor
• Microcontroller is used where ever
Definition
• It is a single chip
• Consists of Cpu, Memory
• I/O ports, timers and other peripherals
Difference
Where ever
• Small size
• Low cost
• Low power
Architecture
•Harvard university
The Architecture given by Harvard University has the following advantages:
1: Data Space and Program Space are distinct
2: There is no Data corruption or loss of data
Disadvantage is:
1: The circuitry is very complex.
Features
• 8 bit cpu
• 64k Program memory (4k on chip)
• 64k Data memory
• 128 Bytes on chip
• 32 I/O
• Two 16 bit timers
• Full duplex UART
• 6 Source/5 Vector interrupts with two level priority levels
• On chip clock Oscillator.
Overview of 8096 16 bit microcontroller
Features
• 232 Byte Register File.
• Register to Register Architecture.
• 10 bit A/D Converter with S/H.
• Five 8 bit I/O ports.
• 20 Interrupt Sources.
• Pulse Width Modulation Output.
• High speed I/O subsystem.
• Dedicated Baud Rate Generator.
• Full Duplex Serial Port.
• 16 bit Watchdog Timer.
Introduction
• The MSC-96 family members are all high performance microcontroller with a 16 bit CPU and atleast 230 bytes of on-chip RAM.
• Intel MSC-96 family easily handles high speed calculations and fast input/out operations.
• All of the MCS-96 components share a common instruction set and architecture.
• However the CHMOS components have enhancements to provide higher performance with lower power consumption.
• These microcontroller contains dedicated I/O subsystem and perform 16-bit arithmetic instructions including multiply and divide operations.
• CPU: The major components of the MCS-96 CPU are the Register File and the Register / Arithmetic Logic Unit (RALU).
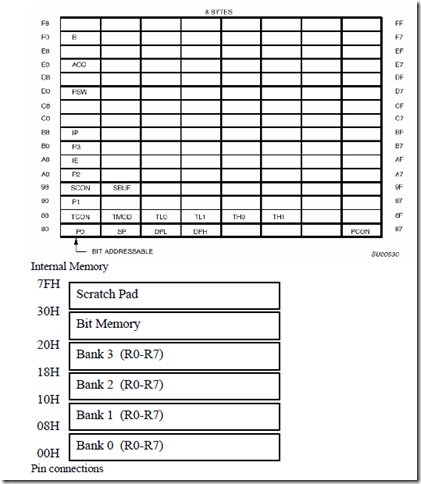
• Location 00H through 17H are the I/O control registers or Special function registers (SFR).
• Locations 18H and 19H contains the stack pointer, which can serve as general purpose RAM when not performing stack operations.
• The remaining bytes of the register file serve as general purpose RAM, accessible as bytes, words or double-words.
• Calculations performed by the CPU take place in the RALU. The RALU contains a 17bit ALU, the program status word (PSW), the program Counter (PC), a loop counter and three temporary registers.
• The RALU operates directly on the Register Files, thus eliminating accumulator bottleneck and providing for direct control of I/O operations through the SFR.