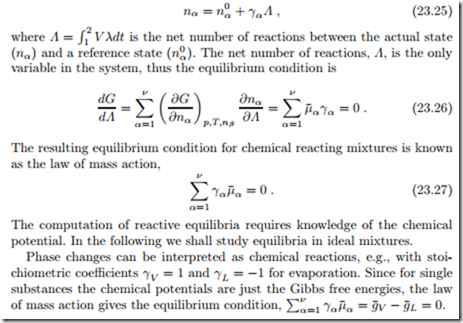
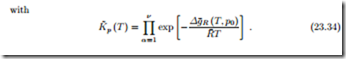Law of Mass Action
In equilibrium at constant pressure and temperature, the Gibbs free energy assumes a minimum, G (T, p, nα) −→ min. In a chemical reaction, the mole numbers nα are related by stoichiometry. From the mole balance (23.8) fol- lows
Law of Mass Action for Ideal Mixtures and Ideal Gases
For ideal mixtures the chemical potential is given by R¯T ln Xα, and the law of mass action gives
Related posts:
Steam and Hot-Water Space Heating Boilers:Steam and Hot Water Boiler Similarities and Differences
Introduction HEATING AND VENTILATING SYSTEMS
SAFETY ON THE JOB:SOLVENTS AND DETERGENTS
Example: Ramjet
Ventilation and Exhaust Fans:Determining CFM by the Air-Change Method
Oil Burners:Priming Fuel Pumps and Adjusting Fuel Pump Pressure.
Open Systems:Flows in Open Systems.
Examples of Reversible Processes in Closed Systems.
Electric-Fired Furnaces - CIRCUIT BREAKERS