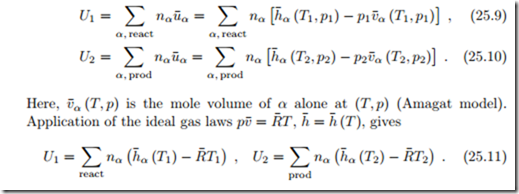Closed System Combustion
For a combustion process in a closed system, the integrated first law gives (kinetic and potential energies ignored)
As for enthalpies, the internal energies must be taken with respect to proper reference data, and the best way to ensure this is to determine them from enthalpies.
For ideal mixtures, which exhibit neither enthalpy nor volume of mixing, we have
Example: Closed System Combustion
As an example we consider the isochoric and adiabatic combustion of mol of methane with nO2 = 9 mol of oxygen (XCH4 = 0.1, XO2 = 0.9) in a closed container, the initial temperature is T1 = 25◦C and the initial pressure is p1 = 10 atm. Reactants and products are considered as ideal gases.
The chemical equation for this reaction is