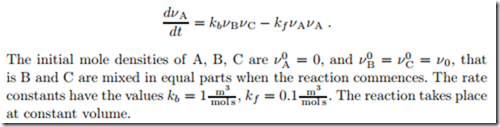Problems
Velocity of Reactions
Consider a reaction of the type A 1→ B + C which occurs according to dnA =−k nA (decay of A). Compute the mole density of A as a function of time, when the initial mole density of A is n0 , and neither B nor C are present initially. Assume constant volume.
Velocity of Reactions
Consider a reaction of the type B + C 0:: 2A which occurs according to
1. Derive the law of mass action for this reaction, and compute the equilibrium mole densities.
2. Compute the mole density of A as a function of time, and also compute the mole densities of B and C as functions of time.
3. Plot νA and νB as functions of time.
Related posts:
Other Automatic Controls:Transformers
Gas-Fired Furnaces
Special Applications:The Ground as Heat Source and Sink
Radiators, Convectors, and Unit Heaters:Kickspace Heaters
Heat Pumps:High-Pressure Switch and Low-Pressure Switch
EPA REFRIGERATION HANDLERS:FREON® REFRIGERANTS
Gas and Oil Controls:Pressure Switches
Water Heaters:Assembly and Installation of Manual Water Heaters
Reversible Processes in Closed Systems:Standard Processes and Basic Equations.