Barometers
Introduction
A barometer is an instrument for measuring atmospheric pressure. It is affected by seasonal changes of temperature. Barometers are therefore also used for the measurement of altitude and also as one of the aids in weather forecasting. The value of atmospheric pressure will thus vary with climatic conditions, although not usually by more than about 10% of standard atmospheric pressure.
Construction and principle of operation
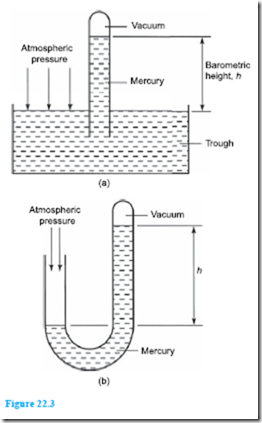
A simple barometer consists of a glass tube, just less than 1 m in length, sealed at one end, filled with mercury and then inverted into a trough containing more mercury. Care must be taken to ensure that no air enters the tube during this latter process. Such a barometer is shown in Figure 22.3(a) and it is seen that the level of the mercury column falls, leaving an empty space, called a vacuum. Atmospheric pressure acts on the surface of the mercury in the trough as shown and this pressure is equal to the pressure at the base of the column of mercury in the inverted tube, i.e. the pressure of the atmosphere is supporting the column of mercury. If the atmospheric pressure falls the barometer height h decreases. Similarly, if the atmospheric pressure
rises, then h increases. Thus atmospheric pressure can be measured in terms of the height of the mercury column. It may be shown that for mercury the height h is 760 mm at standard atmospheric pressure, i.e. a vertical column of mercury 760 mm high exerts a pressure equal to the standard value of atmospheric pressure.
There are thus several ways in which atmospheric pres- sure can be expressed:
Standard atmospheric pressure
= 101325 Pa or 101.325 kPa
= 101325 N/m2 or 101.325 kN/m2
= 1.01325 bars or 1013.25 mbars
= 760 mm of mercury
Another arrangement of a typical barometer is shown in Figure 22.3(b) where a U-tube is used instead of an inverted tube and trough, the principle being similar.
If, instead of mercury, water was used as the liquid in a barometer, then the barometric height h at standard atmospheric pressure would be 13.6 times more than for mercury, i.e. about 10.4 m high, which is not very practicable. This is because the relative density of mer- cury is 13.6.
Types of barometer
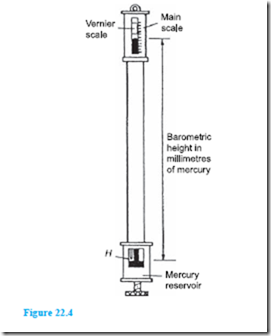
The Fortin barometer is an example of a mercury barometer that enables barometric heights to be measured to a high degree of accuracy (in the order of one-tenth of a millimetre or less). Its construction is merely a more sophisticated arrangement of the inverted tube and trough shown in Figure 22.3(a), with the addition of a vernier scale to measure the barometric height with great accuracy. A disadvantage of this type of barometer is that it is not portable.
A Fortin barometer is shown in Figure 22.4. Mercury is contained in a leather bag at the base of the mercury reservoir, and height, H, of the mercury in the reservoir can be adjusted using the screw at the base of the barometer to depress or release the leather bag. To measure the atmospheric pressure the screw is adjusted until the pointer at H is just touching the surface of the mercury and the height of the mercury column is then read using the main and vernier scales. The measurement of atmospheric pressure using a Fortin barometer is achieved much more accurately than by using a simple barometer.
A portable type often used is the aneroid barometer. Such a barometer consists basically of a circular, hollow,
sealed vessel, S, usually made from thin flexible metal. The air pressure in the vessel is reduced to nearly zero before sealing, so that a change in atmospheric pressure will cause the shape of the vessel to expand or contract. These small changes can be magnified by means of a lever and be made to move a pointer over a calibrated scale. Figure 22.5 shows a typical arrangement of an aneroid barometer. The scale is usually circular and calibrated in millimetres of mercury. These instruments require frequent calibration.