Today is a new day. This is a great branch of classical mechanics, fluid mechanics.
We’ll begin our course with The principle of Archimedes.
When it was first proposed to build ships
made of iron many people laughed at the suggestion.
Owing to the fact that a piece of iron sinks when placed
in water they held the view that iron ships would be a
failure.
When anything is placed in a liquid it
receives an upward force or upthrust. Today we shall
describe a number of experiments to investigate the
forces exerted on a body which is immersed or is floating
in a liquid.
Apparent loss in weight
A simple but striking experiment to illustrate
the upthrust ( buoyant) exerted by a liquid can be shown by tying a
length of cotton to a brick. Any attempt to lift the brick
by the cotton fails through breakage of the cotton, but if
the brick is immersed in water it may be lifted quite
easily. The water exerts an upthrust on the brick, and so
it appears to weigh less in water than in air.
Stone boulders immersed in water have an
upthrust on them equal to about four-tenths of their
weight. This explains why boulders can be moved so
easily by flood water.
In July 1952, for example, a disastrous flood carried debris
containing boulders
weighing up to 20 t each into the streets of Lynmouth in
Devon. Totally immersed they had an apparent weight
of only about 12 t, and thus were more easily
transported by the force of moving water.
Heavily shingle piles up on a sea-beach for
the same reason.
Archimedes’ principle
Experiments to measure the upthrust of a
liquid were first carried out by the Greek scientist
Archimedes, who lived in the third century B.C. The
result of his work was a most important discovery which
is now called Archimedes’ principle. In its most general
form, this states:
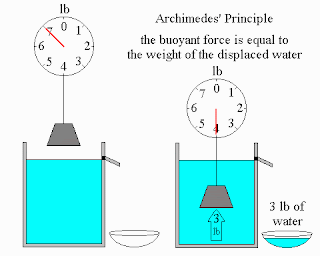
When a body is wholly or partially immersed in
a fluid it experiences an upthrust ( or : buoyant force)
equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
It should be noticed that the word ” fluid ” is
used in the above statement. This word means either a
liquid or a gas.
The application of Archimedes’ principle to gases will be discussed later.
To verify Archimedes’ principle for a body in liquid
A eureka ( or displacement) can is placed on
the bench with a beaker under its spout. Water is
poured in until it runs from the spout. When the water
has ceased dripping the beaker is removed and replaced
by another beaker which has been previously dried and
weighed.
Any suitable solid body, e.g., a piece of metal
or stone, is suspended by thin thread from the hook of a
spring-balance and the weight of the body in air is
measured. The body, still attached to the balance, is
then carefully lowered into the displacement can. When
it is completely immersed its new weight is noted.
The displaced water is caught in the weighed
beaker. When no more water drips from the spout the
beaker and water are weighed.
The results should be set down as follows:
Weight of body in air =…. Newtons
Weight of body in water = …. Newtons
Weight of empty beaker = …. Newtons
Weight of beaker plus displaced water = …. Newtons
Apparent loss in weight of body =…. Newtons
Weight of water displaced =…. Newtons
The apparent loss in weight of the body, or
the upthrust on it, should be equal to the weight of the
water displaced, thus verifying Archimedes’ principle in
the case of water. Similar results are obtained if any
other liquid is used.
To measure the relative density of a solid by using
Archimedes’ principle
What is the density ?
The density of a substance is defined as its
mass per unit volume.
The symbol used for density is the Greek letter ρ (rho).
Thus,
density = mass / volume
or in symbols ρ = m/V kg/ m³
What is the relative density?
The relative density of a substance is the ratio of the mass of any
volume of it to the mass of an equal volume of water, or
relative density = mass of any volume of substance/ mass of an equal volume of water
Since the mass of a body is proportional to its weight,
relative density = weight of any volume of substance/ weight of an equal volume of water
This explains why relative density has also been called specific gravity; the word gravity implying weight.
Archimedes’ principle gives us a simple and accurate method for
finding relative density of a solid.
If we take a sample of the solid and weigh it first in air and then in water the apparent loss in weight, obtained by subtraction, is equal to the weight of a volume of water equal to the sample.
Therefore we may write,
relative density of a substance = weight of a sample of the substance / apparent loss in weight of the sample in water.
Coming up : The applications of Archimedes’ principle to gases with, of course, worked examples 🙂 . Good luck to you all.

