Microprocessors and Microcomputers
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
An integrated circuit is a circuit consisting of different electronic components and the connections between them, which has been produced on the surface of a small flat piece of semiconductor material. An integrated circuit is sometimes called an IC .
A semiconductor is a substance which conducts electricity but not as well as metals do.
The substance usually used for integrated circuits is silicon . A piece of silicon with a circuit on it is called a chip.
Fig 3 Integrated circuit package. This particular type of package has a window, through which are visible the chip itself and the wires connecting this to the pins.
Each integrated circuit is usually encased in a rectangular plastic ‘package’ with two rows of pins to connect the integrated circuit to other circuits. This connection is usually done by soldering the pins into holes on a printed circuit board (see Fig 3 and Fig 4).
Fig 4 Printed circuit board with integrated circuits soldered on to it
MICROPROCESSORS
A microprocessor is an integrated circuit which contains the control unit, the arithmetic and logic unit and possibly some main store for a computer.
A microcomputer is a computer for which the main processing is done by a microprocessor.
Small computers which are not microcomputers are usually called minicomputers. Large powerful computers with a range of peripherals are called mainframe computers.
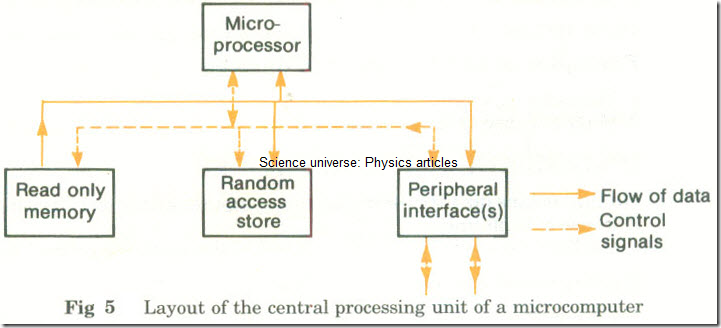
Layout of the central processing unit of a microcomputer
Fig 5 Layout of the central processing unit of a microcomputer
Dedicated microprocessors
A dedicated computer is one which is just used for one particular job. Examples of dedicated microprocessors are:
1 A microprocessor can be used to operate the dashboard and some of the controls in a car. Its tasks may include:
(a) Checking that the seat belts for occupied seats are in use before the engine is started.
(b) Monitoring the fuel mixture so that the engine runs economically.
2 A camera may contain a microprocessor to control exposure calculations. This may make it possible to:
(a) Operate the camera in several different programmed modes.
(b) Select several different points in a picture and have an average exposure calculated for them.